+86 15921716191
+86 15921716191
Leave Your Message
-
 Contact WhatsApp
Contact WhatsApp -
 Contact Phone
Contact Phone -
 Contact Email
Contact Email



In today's fast-paced industrial landscape, RFID labeling systems for industry present a transformative solution. Recent industry reports indicate that the global RFID market is projected to reach $40 billion by 2025, driven by increased adoption in various sectors like manufacturing and retail. Companies recognize the potential of RFID to streamline operations and enhance inventory accuracy.
Despite the advantages, challenges remain. Many businesses grapple with integrating RFID technology into existing systems. The initial investment can be a barrier, especially for small to medium enterprises. Activity data from multiple sources suggest that about 30% of RFID implementations fail to meet expectations. This requires reflection on strategy and execution.
As industries evolve, embracing RFID labeling systems for industry is crucial. Proper implementation can reduce errors and improve efficiency. Yet, companies must proceed with caution. Solid planning and staff training are necessary for success. RFID technology offers immense potential but success demands a thoughtful approach.

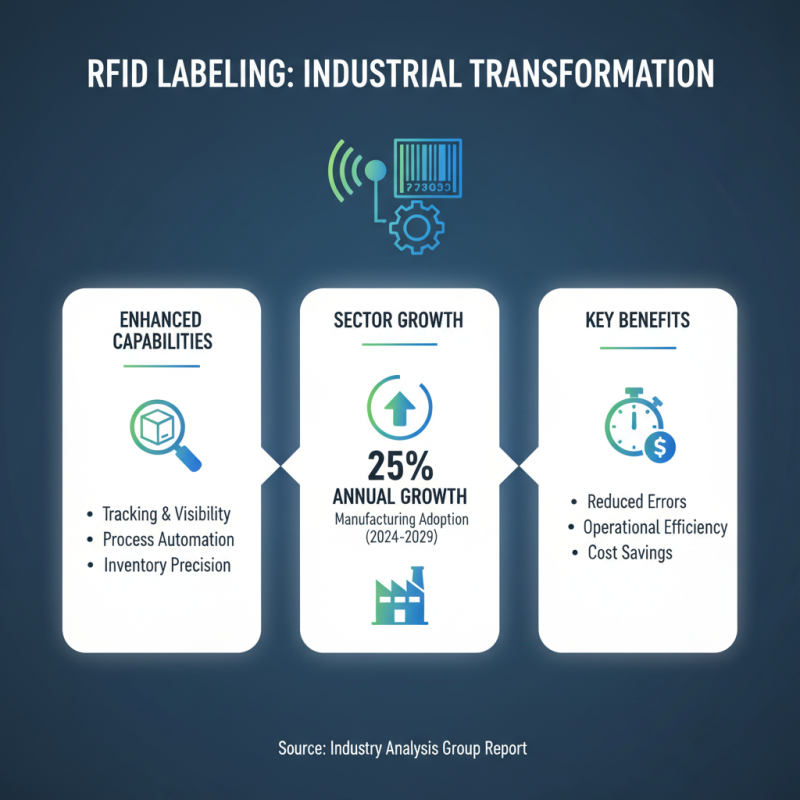
RFID labeling systems are transforming industrial applications. They offer enhanced tracking, automation, and inventory management. A recent report from a leading industry analysis group indicates that RFID adoption in manufacturing is expected to grow by 25% annually over the next five years. This growth highlights the technology's importance in modern operations.
Implementing these systems is not without challenges. Many companies face integration issues with existing infrastructure. The initial setup costs can deter smaller firms. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh these hurdles. RFID systems can cut labor costs by as much as 30%. These savings can redirect resources towards innovation and efficiency improvements.
In addition, the accuracy of data is a concern. Poor label quality can lead to scanning errors. A study showed that 15% of RFID implementations suffer from data accuracy issues. Companies must prioritize quality control to reap the full advantages of RFID technology. Investing in reliable printing and encoding solutions is crucial for maximizing operational effectiveness.
RFID labeling systems are increasingly vital in industry. They streamline operations and improve inventory management. Understanding their key components helps in effective implementation.
At the core of these systems are RFID tags. These tags store important data. They can be attached to products, pallets, or even shipping containers. Each tag has an antenna for communication. This allows for quick scanning and tracking. Readers pull data from tags. They can be fixed or handheld devices. Both have distinct applications in various environments.
Another element is the software that manages the data. This software analyzes the information captured by the readers. It helps in identifying trends and managing stock levels. Users often find the integration with other systems challenging. This can slow down the process. Every system requires some degree of customization, yet this can complicate initial setup. Monitoring these systems is crucial. Regular audits ensure both the hardware and software run smoothly. RFID labeling systems promise efficiency, but they also demand meticulous planning and adjustment.
| Component | Description | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| RFID Tags | Small devices that store data and communicate with RFID readers. | Durability, read/write capability, varying frequencies. | Inventory management, access control, asset tracking. |
| RFID Readers | Devices that emit radio waves to communicate with RFID tags. | Wired and wireless options, handheld and fixed models. | Data collection, inventory audits, supply chain monitoring. |
| Middleware | Software that integrates RFID systems with existing applications. | Data aggregation, processing capabilities, user-friendly interface. | ERP integration, data analysis, reporting tools. |
| RFID Printers | Printers that can print and encode RFID labels simultaneously. | High-speed printing, versatile label sizes, UV durability. | Label creation, asset tagging, production line labeling. |
| Antenna | Transmits and receives signals from RFID tags to readers. | Range variety, directional options, compact design. | Data capture in warehouses, point of sale, event tracking. |
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) labeling brings significant advantages for various industries. It enhances inventory accuracy, reduces costs, and increases operational efficiency. According to a report by the RFID Research Network, businesses can reduce inventory discrepancies by up to 30%. This improvement leads to better stock management and fewer lost sales.
Implementing RFID systems can be challenging. Initial costs and training may deter some companies. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh these hurdles. For instance, a study from the Global RFID Association found that companies adopting RFID saw an average return on investment within two years. This includes lower labor costs and faster processing times.
Accuracy is crucial in manufacturing and logistics. RFID technology provides real-time tracking, which significantly improves workflow. Companies can track items as they move through the supply chain. Yet, not all RFID solutions fit every operation. Customization is key. Businesses must carefully evaluate their specific needs and processes.
When selecting an RFID labeling system, several critical factors come into play. The frequency of the RFID tags is crucial. Low-frequency tags can penetrate materials better, while high-frequency tags offer better data transfer speeds. A study by Allied Market Research shows that the RFID market is projected to reach $42 billion by 2027, indicating its growing relevance.
Another important factor is the compatibility of the labeling system with existing infrastructure. Many companies struggle with integration, which can hinder operational efficiency. Compatibility issues can lead to underutilization of the RFID system. Recent research highlights that about 30% of companies cite integration challenges as a major obstacle when adopting new technologies.
Cost is also a significant consideration. It’s easy to be tempted by low upfront pricing, but hidden costs can emerge later. These include maintenance fees or the need for additional hardware. A survey found that 65% of users underestimated the total cost of ownership, leading to potential budget overruns. In this complex landscape, weighing all aspects carefully is vital for effective decision-making.
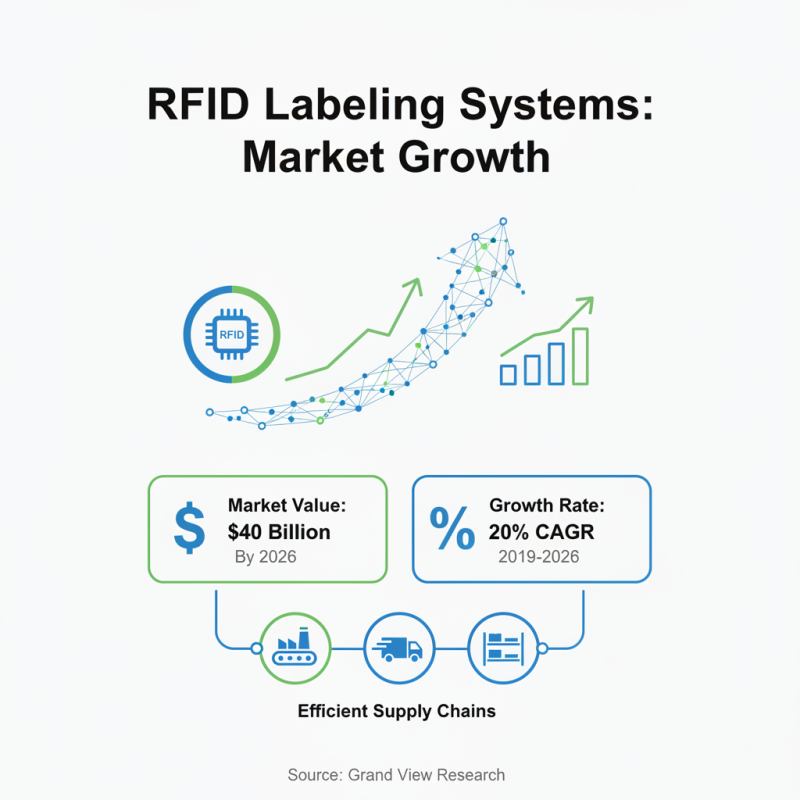
RFID labeling systems have become crucial in modern industries. According to a report by Grand View Research, the RFID market is projected to reach $40 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 20%. This rapid growth highlights the importance of efficient labeling systems in supply chains.
Key features of these systems include read range, data storage, and durability. Systems with longer read ranges can enhance efficiency. Some may read tags from over 20 feet away. However, not all industries require such distance. Ease of integration with existing software also affects adoption. Systems that can easily sync with inventory management tools can save time.
While RFID labeling helps in tracking assets, some challenges exist. Cost can be prohibitive for smaller businesses. A report from Allied Market Research suggests that initial setup costs can deter adoption. Moreover, RFID tags can be sensitive to environmental conditions, leading to operational inefficiencies. As technology evolves, addressing these issues is essential for broader acceptance and functionality.